|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
 |
|
Welcome
We enjoyed seeing many of you at the Atlanta ASMS conference. If you missed our breakfast meetings, we have summaries of the two Matrix Science presentations.
Mascot tip of the month highlights a few Mascot Server features that can only be configured from within a quantitation method.
Please have a read and feel free to contact us if you have any comments or questions. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Metaproteomics with Mascot Server
Investigating the microbial communities present in complex samples such as peat bogs, ocean water, or gastric systems creates new challenges for protein identification.
- There is no way to know all the microbial species present in the sample
- Most microbes have no reference genome
- Many species are similar making it harder to classify a hit
- Chimeric spectra are more common due to peptide homology across the many species
Using a human gut data set, we explored a strategy to get the maximum information out of the data. The first step was to create a suitable database using public databases and knowledge about the microbial environment. Then, we added entries from the matched metagenome. It is important to include the host organism (if appropriate) and a contaminants database, but try to keep the search space as small as possible.
An example search resulted in 5059 PSM's at 1% FDR and 1357 protein hits. About a third of these matches were to the matched metagenome.
Go here to read more details about the parameters, process, and taxonomic filtering of the results.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Middle-Down searching
Searching the larger peptides produced by enzymes such as Lys-C or Asp-N can lead to reduced inference problems and more confident assignment of proteoforms. Sample processing is generally trickier than bottom-up (though easier than top-down), and you need to make sure you've got your database and search conditions set up correctly.
With longer peptides, the parameters that probably need adjustment in the spectral processing are the charge state values for the precursor and the MS/MS fragments. You may also want to de-charge the peak list outputs to MH+ values and create a new instrument definition that only looks for singly charged fragments.
We examined a middle-down dataset comprised of Histone H4 from 2 cell lines, one pre-cancer cell line and one breast cancer cell line. This was a block and release experiment with samples taken when the cells were in S-phase and the G2/M phase.
Across the two cell lines, we identified 229 proteoforms including 127 different possible proteoforms in the asynchronous datasets, 178 identified in S-phase and 169 in G2/M phase.
Read more here about how to achieve higher confidence in proteoform identifications using middle-down approaches.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mascot Tip
There are a few Mascot Server features that can only be enabled or configured from within a quantitation method. These may be useful even if you are not intending to use Mascot to perform quantitation. To view the examples mentioned below or to configure your own method, follow the Configuration Editor link from your local Mascot Server home page.
Exclusive modifications: This is where a given peptide may carry one or another set of modifications, but never a mixture. Dimethylation [MD] is a good example. One peptide might have any K and its N-term modified by Dimethyl. Another peptide might have K and N-term modified by Dimethyl:2H(4). But, you will never see a peptide with an unmodified K or N-term or a mix of light and heavy modifications. Note that the method must also set constrain search to be true. Otherwise, the search treats exclusive modifications as variable and only applies the exclusive filter during quantitation.
Two modifications at a single site: With Mascot Server 2.4 and later, variable modifications can be 'in addition' to the exclusive modifications defined in a quantitation method. This is mainly useful for SILAC, and avoids having to define combination modifications, such as Label:13C(6)+Acetyl. The search must also include the parameter MULTI_SITE_MODS=1, which has to be added to the top of the MGF peak list unless you are using Mascot Daemon or Mascot Distiller to submit the search.
Stable isotope labelling: If you need to match peptides that have been metabolically labelled, this can only be specified in a quantitation method. For an example of double labelling, see 15N + 13C Metabolic [MD].
For more information on all of these features, see this blog article and the main help page for quantitation method configuration.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Please contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|
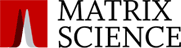 |
 |
|
|