|
To view this email as a web page, click here. |
|
|
|
Welcome
When you process raw data into peak lists, we recommend always calculating ion intensity from the peak area. The alternative – signal-to-noise ratio – may be useful with diagnostic ions.
In this month's highlighted publication, unlabeled and deuterium-labeled samples are duplexed with dimethyl labeling to measure protein turnover rates.
Mascot Server has a role-based access mechanism that is useful in a variety of situations.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Mascot: The trusted reference standard for protein identification by mass spectrometry for 25 years
|
Get a quote
|
 |
|
|
|
Ion intensity: peak area or signal to noise ratio?
|
|
|
When raw MS/MS signal is saved in profile mode, it must be processed into peak lists before peptide identification.
A peak detection algorithm assigns m/z and intensity for each ion in the spectrum.
There are a few ways to compute ion intensity from the raw signal, and the choice influences the identification results.
The two common approaches are using peak area as ion intensity, or using the peak's signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio.
The choice was explored in a recent paper by Hijazi et al. (Mind Your Spectra: Points to be Aware of When Validating the Identification of Isobaric Histone Peptidoforms. J Proteome Res. 2025), where the authors studied diagnostic ions from highly modified histones.
The intensity of low-mass diagnostic ions was apparently suppressed when compared to the raw data, while the higher mass peptide fragments were closer to the raw trace.
Switching to S/N as ion intensity reversed the situation.
The reason is, the lower mass diagnostic ions, while having a high maximum intensity, are in fact very narrow, so they have a limited amount of total signal (peak area) but very good S/N.
Some software packages don't give a choice or may default to using S/N ratio.
Mascot Distiller defaults to using peak area, but you can switch it to using S/N ratio.
We reprocessed the data with both.
In short, using peak area gives the most accurate representation of the actual signal in the spectra, leading to better Mascot results.
To prioritise or boost diagnostic ions, you may wish to use S/N and accept the slight reduction in the quality of the search results.
The full results are in our blog.
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Featured publication using Mascot
Here we highlight a recent interesting and important publication that employs Mascot for protein identification, quantitation, or characterization. If you would like one of your papers highlighted here, please send us a PDF or a URL.
|
|
|
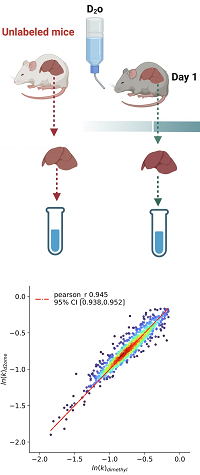
Duplexing metabolic deuterated water-labeled samples using dimethyl labeling to estimate protein turnover rates
Henock M. Deberneh, Michael E. Taylor, Kamil A. Kobak, Michael T. Kinter, Benjamin F. Miller, Rovshan G. Sadygov
Communications Chemistry 8, Article number: 375 (2025), doi:10.1038/s42004-025-01762-1
Metabolic labeling with deuterated water alters the isotope profile of enzymatically digested peptides, and protein turnover rate can be estimated by modeling the time course of the monoisotope's relative abundance depletion.
Traditionally, unlabeled and deuterated water-labeled samples are analysed in separate LC-MS/MS runs, followed by data normalisation for label enrichment.
In this study, the authors duplex the unlabeled and deuterated samples using light and heavy dimethyl labels, which allows running them as a single LC-MS/MS experiment.
This enables computation of fractional syntheses and direct comparison of isotope distributions.
Mice were given a low-fat diet with D2O-enriched drinking water at staggered intervals.
Liver and plasma samples were prepared and analyzed with LC-MS/MS (Thermo Orbitrap Exploris) in DDA mode, then searched using Mascot Server.
Dimethyl labels were selected as variable modifications, combined with #13C parameter increased to 2, allowing identification of precursors from higher mass isotopomers.
Turnover rates were then computed using in-house software (d2ome-dimethyl).
The number of peptide identifications in dimethyl duplexed samples was lower than non-duplexed samples due to increased proteome complexity.
However, the computed turnover rates from two-sample and one-sample approaches were in good agreement (Pearson correlation 0.945).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Role-based access with Mascot Security
|
|
|
Mascot Server has a built-in, role-based access mechanism called Mascot Security.
Role-based access has a variety of use cases.
Password protected administration: When you activate Mascot Security, all configuration is protected by the admin account password.
Enable the 'guest' account to allow users to submit and view searches without a password.
Visibility and privacy settings: Users can be assigned into groups.
The privacy settings control whether users in different groups are allowed to see each other's search results.
Setting priorities and limits: Users and groups can be given higher or lower access to computational resources,
as well as limiting the duration or size of database searches.
More detailed examples are in the Security section in the online help.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
About Matrix Science
Matrix Science is a provider of bioinformatics tools to proteomics researchers and scientists, enabling the rapid, confident identification and quantitation of proteins. Mascot continues to be cited by over 2000 publications every year. Our software products fully support data from mass spectrometry instruments made by Agilent, Bruker, Sciex, Shimadzu, Thermo Scientific, and Waters.
Get a quote
|
|
|
You can also contact us or one of our marketing partners for more information on how you can power your proteomics with Mascot.
|




|
|
|
|
|